Scientists have reconstructed the habitat of ancient people
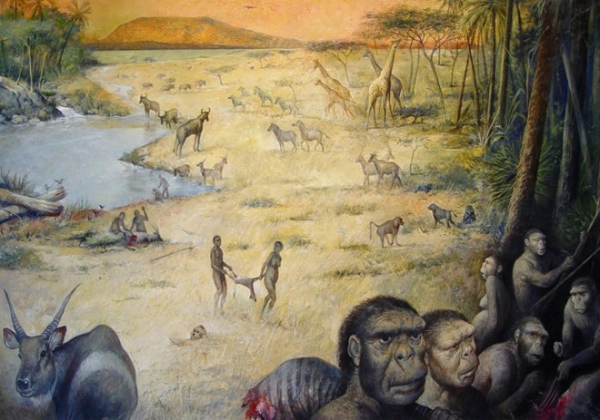

The habitat of ancient people in the view of the artist.
M. Lopez-Herrera / The Olduvai Paleoanthropology and Paleoecology Project and Enrique Baquedano
An international team of historians and geologists reconstructed the natural landscape that existed 1.8 million years ago at Olduvai gorge in Tanzania. Here were found the remains of ancient human ancestors, who lived in the gorge during this period. With the reconstruction, the scientists were able to understand the conditions in which lived ancient hominids. The study is published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, briefly about the study described in the press release .
Excavations at Olduvai gorge began in the 1930-ies. During excavations 1959 — 1963 anthropologists Louis and Mary Leakey discovered in the gorge, the remains of Homo habilis, Homo habilis, and a representative of the suborder Australopithecus, Paranthropus boisei, whose age was estimated at 1.9 and 1.8 million years, respectively.
In 1994 excavations began again, on the shores of an ancient lake that existed 1.8 million years ago. Now scientists have discovered numerous well-preserved animal bones and remains of plants that existed at the same time, when in the gorge lived hominini. In the eruption of the volcano, which is located 16 kilometers from the gorge, ash covered the surface of the earth, protecting the organic remains and animal bones from decay. Researchers have detected the bones of giraffes, elephants and antelopes, and from plants – the remains of palm trees, Acacias, ferns and macrophytes with floating leaves. As a result, scientists were able to make a “map” and put on her place, where they found the plants, animal bones and remains of prehistoric people.
The authors believe that hominini killed prey in other locations or picked up the carcass left by lions or hyenas, and brought her to the shore of the lake to eat in a secluded spot under the protection of palm trees and Acacias. In their diet could include ferns, crustaceans, snails and slugs. Perhaps the ancient primates had to compete for prey with other predators that were unsafe. “We don’t think hominina lived here. Rather, they used a nearby source of fresh water,” says one of the authors, Professor Ashley of the University of Rather.
Homo habilis, Homo habilis, inhabited by 2.8 to 1.5 million years ago.Paranthropus boisei from Australopithecus suborder, lived in the period 2.3 — 1.2 million years ago.