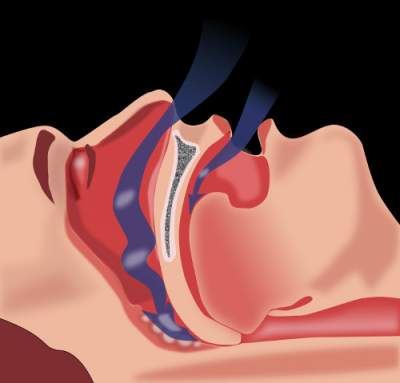
 Obstructive Apnea Sleep Hypopnea (OAHS), also called night or sleep apnea occurs due to obstruction of passage of air through the airway at the level of the pharynx during sleep.
Obstructive Apnea Sleep Hypopnea (OAHS), also called night or sleep apnea occurs due to obstruction of passage of air through the airway at the level of the pharynx during sleep.
Obstacle to air flow can serve as the root of the tongue, the soft palate or the epiglottis, which are displaced posteriorly under the influence of its own weight in the position of a man lying on his back. Additional reasons for the narrowing of the lumen of the respiratory tract are the proliferation of lymphoid tissue, obesity in the neck, expansion of the venous plexus and congenital anomalies in the neck and mandibular area.
OAHS most often occurs in men aged 34-65 years, with excess body weight and increased the size of the neck (“double chin”).
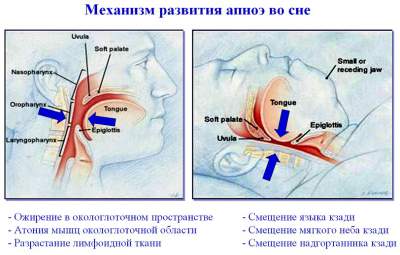 The mechanism of the development of sleep apnea
The mechanism of the development of sleep apnea
The obstruction of the respiratory flow during sleep occurs gradually over several years. Partial narrowing of the respiratory lumen at the level of the pharynx is accompanied by severe snoring, caused by vibration of the soft tissues on the inhale and the exhale. When you snore in the lungs comes the reduced amount of air and oxygen (hypopnea), while the patient experiences the initial signs of developing hypoxia. Appear moderate headaches in the morning, cardiac arrhythmia and arterial hypertension.
The progression OAHS there are episodes of sleep apnea – breathing stops with the complete closure of the lumen of the pharyngeal soft tissues. Episodes of apnea can last from 10 seconds to 1 minute are observed from 5 to 100 times per hour and more. Respiratory failure accompanied by awakening of the patient and disrupt natural sleep patterns.
The final result of many revivals when apnea is severe daytime sleepiness. The patient may fall asleep at work, in transport, driving a car.
OAHS requires comprehensive diagnosis and therapy with CPAP devices, and oxygen concentrators. Inattention to snoring and night apnea patient threatens a wide range of dangerous symptoms (headache, high blood pressure, arrhythmia), causes drowsiness and incapacity in the daytime.
Night apnea provokes and exacerbates metabolic diseases (diabetes, obesity), increases the risk of development of heart failure and cerebral stroke. The estimated life expectancy in patients with untreated OAHS 25-30 % less compared to patients undergoing CPAP therapy.








