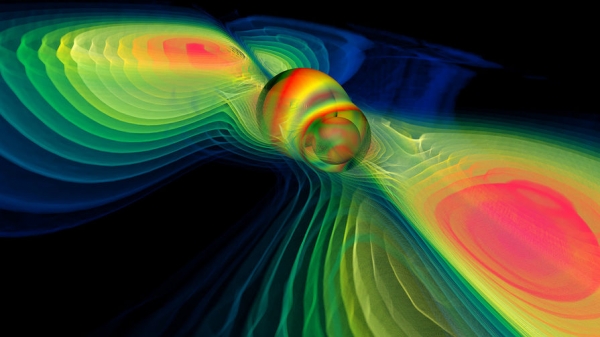
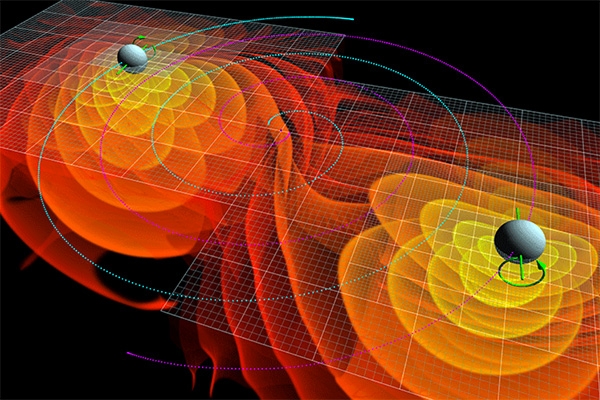
Scientific world is full of excitement: following the discovery of the Higgs boson, the recent history of physics has added yet another achievement. The discovery by scientists of gravitational waves confirmed theoretical calculations Einstein made nearly a hundred years ago. Understand what it is and why it matters.
What happened?
The gravitational waves?
Retrying of failed…
…and good
The merits of Russian scientists
The consequences of opening
1
What happened?
14 September 2015, 13:51 Moscow time the mirrors of the gravitational telescopes near American cities of Livingston and the Hanford recorded gravitational wave, which appeared 1.3 billion years ago due to the marginal convergence and merging of two black holes at a distance of about 50 million light years from Earth. The weight of black holes is enormous: one in 29 of the Sun and the other in 36. After 20 milliseconds after convergence they merge into one bigger black hole, resulting in the spin-off in the collision the excess energy waves shake the space-time.
2
The gravitational waves?
To understand what gravitational waves, imagine a piece of stretched fabric, which in turn put some rocks of different weights. Stone pushes the fabric – the heavier, the stronger. On a cosmic level the role stone can play the black hole (two in our case). Such massive objects cut through the fabric of space-time that make up our world. The fabric ranges appear wave, very weak, and for this reason, almost beyond detection. First to the idea of the existence of gravitational waves came albert Einstein, who expressed it in his theory of relativity.
3
Retrying of failed…
There were attempts, and repeated. Here holds the primacy of physical faculty of Moscow state University: in the 70-ies in the group under the leadership of Professor Vladimir Braginsky performed experiments on the fixation of such waves. Unfortunately, nothing short of seismic noise from the trams calling at the nearby depot, the device did not catch. The experiment was a failure.
In 2015, researchers from an international collaboration of BICEP announced the irrefutable traces of gravitational waves in the relict radiation, which was preserved from the first moments after the Big Bang. But soon, this attempt was disastrous: during the processing of the data, the researchers did not take into account space dust.
4
…and good
LIGO (Laser Interferometer Gravitational-Wave Observatory) is an Observatory established on the basis of international cooperation. The staff of the Observatory consists of scientists from 14 countries. Russia in LIGO represented by two groups: the group from Nizhny Novgorod, led by Alexander Sergeev Institute of applied physics RAS and the group from Moscow led by the Professor of physical faculty of Moscow state University Valery Mitrofanov (until recently – Vladimir Braginsky). LIGO began in 2002, but in 2010 was closed for modernization because of insufficient power. The laboratory was opened in 2014, having at its disposal a much more sophisticated technique. The cost of the project is 620 million dollars, and it should be noted that investors were not confident in the success of the project.
The basis of LIGO is a detector and two of the interferometer, one in Livingston (Louisiana, USA), and the other at the Hanford (Washington, USA). Gravitational waves propagate at the speed of light, and therefore, the signal came to them only with a small delay of 10 milliseconds.
Interferometers – large G-shaped antenna with the shoulders by four kilometers. Inside they collected optical schematic of a high q (i.e. low background noise), in which laser beams are launched. Under the action of gravitational waves one shoulder should be compressed, and the other, conversely, to stretch. As a result, the laser beams go over the shoulders a bit different and the distance to the exit access with a small gap between them. After leaving, they again come together and form an interference pattern, the characteristics of which can be restored by changing the shoulders of the antenna, and what was the gravitational wave, which caused all of this.
5
The merits of Russian scientists
They are significant. Our compatriots developed the telescope design (for example, Russian physicists have proposed to use quartz-purpose thread for hanging mirrors).
The Director of the Observatory, Emeritus Professor at California technical Institute Kip Thorne recognised the particular contribution of our physicists. Thanks to Vladimir Braginsky was found optimal path search of gravitational waves (was able to prove that black holes are sources of such radiation).
6
The consequences of opening
First, it is a new milestone in the observation space, which can be compared with the invention of the telescope. In the long term – development and launch of the space gravitational telescope that will help find the exact coordinates of the wave sources.
Second, scientists will be able to pay close attention to relic gravitational waves, which appeared after Big Bang and thus learn more details about him.
Thirdly, the opening will contribute to the development of the theory of quantum gravity that allows consistent to describe all types of physical interactions