Gradual capacity loss the battery is one of the pressing problems of the industry. Modern lithium-ion batteries, as promised by their developers, can withstand approximately 500-1000 recharge cycles. But a discovery by researchers at the University of California, Irvine may help to increase life cycle of battery is in the tens and hundreds of times.
pubs.acs.org
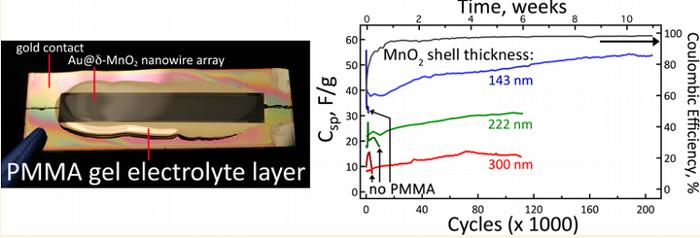
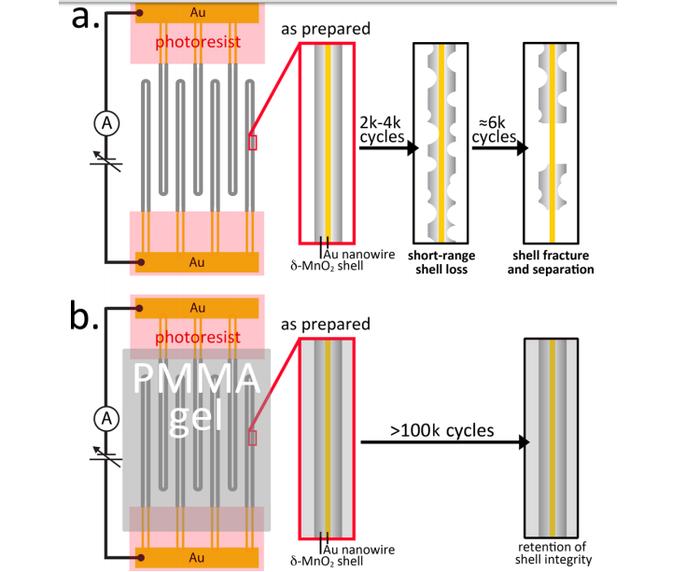
As stated in related scientific publications “100k Cycles and Beyond: Extraordinary Cycle Stability for MnO2 Nanowires Imparted by a Gel Electrolyte”, scientists were able to achieve a substantial increase of the lifetime of the battery by replacing the liquid electrolyte gel electrolyte based on polymethylmethacrylate (PMMA) in the battery with the gold nanowires. Nanowires themselves are covered with a layer of manganese dioxide. For the nanowires with the thickness of the coating of manganese dioxide and 300 nm 222 life cycle was more than 100 thousand cycles of charge-discharge, and record the value of 200 thousand achieved by the use of nanowires with a shell thickness of 143 nm.
pubs.acs.org
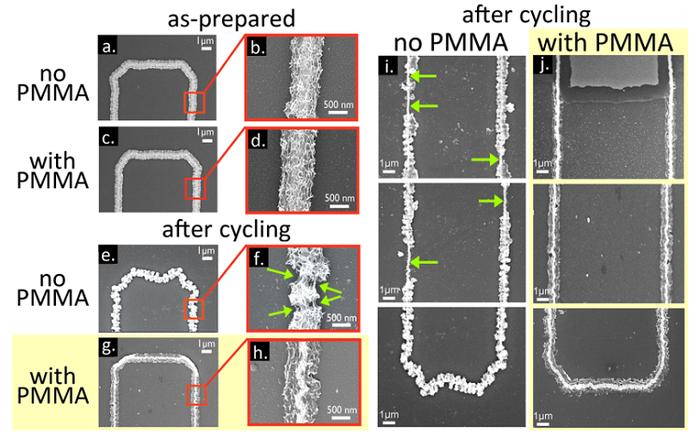
Initially it was an experiment with the use of nanotechnology in batteries. But in the course of the research, the inventors unexpectedly discovered that the battery capacity hardly decreases after a large number of recharges.
pubs.acs.org
Yet scientists themselves are unable to explain this phenomenon. The current output after 100 thousand cycles of charge-discharge remains at 96 %. For the nanowires with a shell thickness of 143 nm after 30-40 thousand cycles, the current output is more than 98 %. In previous experiments using liquid electrolyte life cycle has reached the 2-8 thousand cycles of charge-discharge.
In a scientific publication provides details of production of the gel electrolyte. For this, the inventors added 1.6 grams of poly (methyl methacrylate) to five milliliters of chlorine oxide and lithium in a dry polycarbonate. The mixture was dissolved by heating up to 115 degrees Celsius. In the desiccator (a special vessel for drying) mass was cooled to room temperature, after which it was transformed into a gel-like state.
Note, the serial production of new batteries it does not go. It’s not just the high cost (the use of gold for nanorobotics and high complexity products) — technologically, the production process has not worked.
The developers of rechargeable batteries continuously working on the development of better power sources, since modern batteries in most cases are unable to fully satisfy the consumer. So, Sony has promised to release capacious battery with a solid electrolyte, but it is characterized by a life cycle of only 2 thousand cycles of charge-discharge. At Stanford University proposed a battery with a silicon anode capacity is 10 times higher than typical solutions. But a special “longevity” he is unlikely to differ.