Scientists from Hokkaido University, Tokyo University and Agency for science and technology of Japan made a map of risk of spread of the virus Zeke until the end of 2016 for 189 countries.
According to the analysis of groups of researchers to Maksimalna at risk are countries that border with Brazil, however, in their opinion, fever Zeke necessarily seriously affect Europe.
However, subtropical and tropical countries with a history of dengue fever and other diseases transmitted by mosquitoes, have the greatest risk of spreading the virus when he arrives in the country. This means that many countries in South and Central America and the Caribbean face the greatest risk of infection and should take measures to prevent mosquito bites, according to the study, recently published in “PeerJ”. France, southern China and the UAE also fall into this category, these countries have seen outbreaks of this disease.
“We showed that the predicted risk of transmitting the virus zika countries is higher in tropical and subtropical countries with epidemics of dengue or chikungunya, while the risk of introducing more “scattered” around the world,” said Hiroshi Nishiura, Professor of hygiene at Hokkaido University.
The zika virus was first discovered in Uganda in 1947, and then discovered in 39 countries worldwide, including USA, India and Japan. In early 2015 outbreak of zika in Brazil has caused a large number of cases of microcephaly, a disease in which children are born with abnormally small heads. The relationship between these two diseases is not completely proven but very obvious. After this outbreak in Brazil, the zika virus was detected in 39 countries, including in Europe, South America and Asia.
Many researchers are working to predict the possible spread of the virus zika, especially when you consider that it can be carried out using the infected travelers, which in turn transmit the virus to local mosquitoes. We must realize the danger of problems including because this summer hundreds of thousands of tourists from various countries will participate in the Olympic games in Rio de Janeiro.
Professor Nishiura and his colleagues predicted the probability of spread of the virus zika-based by the end of 2016 using the model of survival analysis, information on transport networks and data transmission of dengue viruses and chikungunya, which are also transmitted using the same species of mosquitoes. They analyzed data up to 31 January 2016, and noted that the results need to listen, because in the following months, the incidence of Zeke confirmed in a larger number of countries.
The authors recommend to conduct a large-scale analysis under the auspices of the who, to more accurately predict the spread of Zeke within regions. For example, models should include information about the populations of mosquitoes and other environmental factors.
“Despite the obvious need to improve forecasts in the future, the present simple, the study has successfully made the global risk prediction of migration and local transmission Zeke,” says Professor Nishiura. “Countries with low risk, in turn, should strengthen the work on prevention among pregnant women who are going to go to epidemically dangerous areas.”
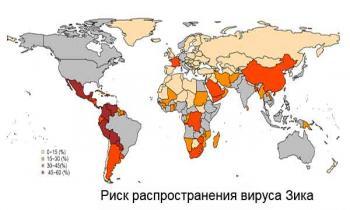
On the map: Global distribution of risk of local transmission of zika virus. Countries are coloured according to the degree of risk (0-15, 15-30, 30-45 and 45-60%, respectively). Brazil and the countries that are already affected by the disease prior to the current migration of the virus out of Brazil, painted in gray.