
The Russian economy remains in the doldrums, the country increases its dependence on raw materials, which may be indicative of structural degradation. These findings are contained in the progress report “Comments on the state and business” experts of the center of Higher school of Economics. According to them, out of the crisis may be delayed.
Economists point out that a raw roll of the domestic economy reached its climax. During the crisis of the commodity sector (mining, cargo handling, agriculture) reached a historically maximum levels, but their dynamics are separate from the main part of the economy. At the same time non-primary sectors has fallen dramatically and are now close to their local minima.
In particular, in comparison with the pre-crisis period, agriculture increased its production volumes by 6.6%, mining increased by 3.6%, and cargo turnover rose by 3.4% (third quarter of the current year to the average level of 2014, after seasonal adjustment).
All other sector during the crisis greatly subsided: manufacturing – 7.2%, wholesale trade – 10.2%, construction – by 12,8%, retail trade – 14,7%, paid services – by 2.4%.
On average, the commodity sector during the crisis increased by 4.0%, non-oil – fell by 9.3%. There is a strengthening of rent bias of the Russian economy, say the authors of the report.
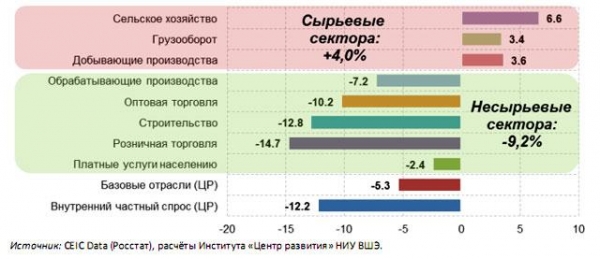 Change of macroeconomic indicators during the crisis (level of the third quarter of 2016 to the average level of 2014, seasonally adjusted), %
Change of macroeconomic indicators during the crisis (level of the third quarter of 2016 to the average level of 2014, seasonally adjusted), %
Experts note that in recent months the raw roll has only increased. “Thus, in the third quarter, agriculture grew by 1.8% (an increase from the previous quarter, seasonally adjusted), extraction of minerals without the contribution of oil services – 1.1% turnover 3.6%. Among non-primary sectors showed a growth of the construction sector: +2.7 percent, after falling 7.7% in the previous quarter,” reads the study.
According to experts, the division of sectors into commodity and non-commodity it is important not only because it allows you to fix the process of “simplification” of the Russian economy and its structural degradation. It also helps to evaluate separately the influence of external or temporary factors (such as growth in external demand for raw materials or a good harvest) and the influence of internal factors (growth of demand in the economy). Depends on interpretation of what is now the state of the Russian economy.
“In quite formal (if not superficial) approach is the fact that in the third quarter, the index of basic industries increased by 0.4% for the second quarter, it is logical to interpret as a sign that the negative trend is broken, and finally began the transition to the phase of cyclical growth. However, as it turns out, almost all contributions have been secured commodity sectors, the dynamics of which almost nothing to do with the General state of the economy; moreover, in subsequent quarters, their contribution is likely to be negative. The same dynamics of non-oil sectors, in reality characterizing the state of the economy does not look very promising,” say the economists.
The report authors also add that the rise in commodity sectors ceteris paribus has a positive impact on the economy, but in the third quarter, the impact of unstable factors was too big.
“Growth has not yet formed. Most likely, the situation will normalize in 2017. For 2016, we maintain our forecast for GDP decline at 0.9%,” – said in the report.
About depression and serious condition of the Russian economy also shows a composite index of regional economic activity (REA), which fell from 49.8 to 38.8 per cent, economists say. Still strong decline in the retail trade, where growth is observed only in every fifth region and paid services (on average grow two regions out of five). In addition, the volume of construction declined by more than two thirds of regions.
“Thus, “spatial” weakness in domestic consumer and investment demand is still not passed, which under adverse circumstances is fraught with a new round of recession”, – experts say.
The report draws attention that in the context of Federal districts, the lowest economic activity was observed in the Ural district on which the composite index CEA was only 15%. Here, the depression spread to all regions, and in the Chelyabinsk region all five sectors of the economy declined in the last three months. An equally unfavourable situation in the Smolensk region and the Republic of Komi, which “pulled down” composite indices of CEA the Central and North-Western districts.
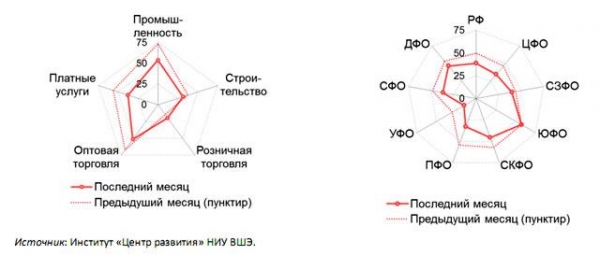
The composite index of regional economic activity (REA), by sectors of the economy and Federal districts (September 2016)
In other Federal districts composite indices of CEA in September, almost simultaneously fell, hitting in the range from 33% (Volga region) to 47% (far Eastern).
The only exception to this almost universal retrograde motion became the southern district, where the composite index of electronics was 58%, and best results were shown by Krasnodar Krai and Sevastopol (growth in four of the five sectors, the index of electronics equal to 80%).
At the level of individual regions, the index in September, REA exceeded 50%, indicating a growth in economic activity, only in 25 cases, and in 57 regions continued to decline.
“This is much worse than it was in August. The share of the regions in which reduced all five sectors of the economy or growing only one of five in September increased markedly, and the share of the regions in which four or five sectors of the economy are growing, remains much lower than is typical of phases of economic growth,” say the authors of the report.
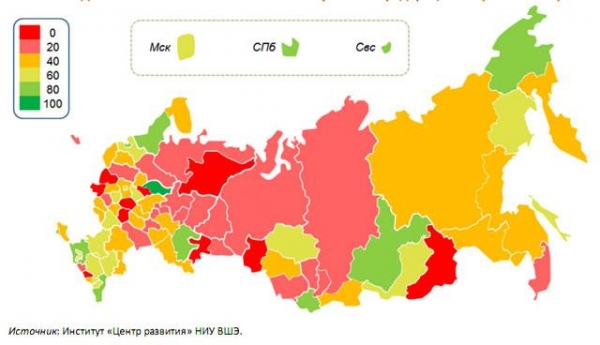
Indices of economic activity in the regions of the Russian Federation (September 2016)
Among the most problematic, at the end of September, experts of the Center for development HSE took ten regions where all the five sectors declining (index REA = 0). This group includes: Bryansk, Ivanovo, Ryazan, Smolensk, Tambov and Chelyabinsk oblast and Zabaykalsky Krai and the Komi Republic and Kabardino-Balkaria. In 21 region of reduced four of the five sectors (index, CEA = 20%). The share of these two groups together account for 32% of GRP of Russia.
Given the significant volatility indices of REA, we can assume that the September decline should be interpreted as a temporary correction, not as a sign of the approaching new round of frontal recession. However, the way out of depression clearly will be very gradual, and may take more than one quarter, economists say.
Experts also note that the new encouraging of the October medium-term forecasts of development of the Russian economy are, at first sight, more positive, particularly from international organizations. But even amid a forecast of optimism Russia in the coming years will reduce its share in global GDP, the report said.








